Pakistanis Are Third Largest Foreign Investors in Dubai Real Estate
Pakistanis have invested $10.6 billion in Dubai real estate, ranking them as the third largest investors in the city on the Gulf. Indian investors lead Dubai real estate investments with $29.8 billion, followed by British investors' $14.7 billion investment.
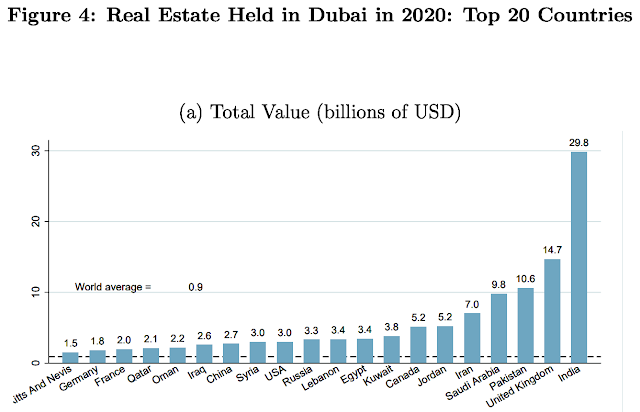 |
| Wealth From Top 20 Countries Invested in Dubai Real Estate. Source: EU Tax Observatory |
With at least $146 billion in foreign wealth invested, the Dubai property market is now the world's largest offshore investment market for foreign investors. It is now twice as large as the London real estate market in terms of wealth invested by foreigners through shell companies. There are nearly 20,000 unique foreign owners of Dubai real estate from Pakistan, the third largest number behind almost 35,000 Indian owners and about 23,000 owners from the United Kingdom, according to the EU Tax Observatory.
 |
| Unique Entities From Top 20 Countries Owning Dubai Real Estate. Source: EU Tax Observatory |
 |
| Money Laundering Risk. Source: FATF |
Related Links:
Haq's Musings
South Asia Investor Review
The West Enables Corruption in Developing Nations
Did Musharraf Steal Pakistani People's Money?
Pakistan Economy Hobbled By Underinvestment
Raymond Baker on Corruption in Pakistan
Nawaz Sharif Disqualified
Culture of Corruption in Pakistan
Convicted Money Launderer Altaf Khanani Has Close Ties to Pakistan Politicians
Zardari's Corruption Probe in Switzerland
Politics of Patronage in Pakistan
British Crime Agency Lists Pakistan Among Top 3 Sources of Money Laundering



Comments
Lahore: Pakistan Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif testified today in a special court hearing in the Pakistan Rupee 16 billion money laundering case against him that he had refused to take any salary when he was the Chief Minister of Pakistan's Punjab province, and called himself a "majnoo" for doing so.
Shehbaz Sharif and his sons - Hamza and Suleman - were charged by Pakistan's Federal Investigation Agency or FIA in November 2020 under various sections of the Prevention of Corruption Act and Anti-Money Laundering Act.
Hamza Sharif is currently the Chief Minister of Pakistan's Punjab province, while Suleman Sharif is residing in the UK.
The FIA investigation has detected 28 benami accounts, allegedly of the Shehbaz family, through which an amount of Pakistan Rupee 14 billion (USD 75 million) was laundered from 2008 to 2018.
The FIA examined the money trail of 17,000 credit transactions.
The amount was kept in "hidden accounts" and given to Shehbaz Sharif in his personal capacity, according to the charges.
"I have not taken anything from the government in 12.5 years, and in this case, I am accused of laundering ₹ 2.5 million," Shehbaz Sharif said during the hearing.
"God has made me the Prime Minister of this country. I am a majnoo (fool) and I did not take my legal right, my salary and benefits," Pakistan's Dawn newspaper quoted him as saying.
He recalled that the secretary had sent a note to him for sugar exports during his tenure as Chief Minister of Punjab province, when he had set an export limit and rejected the notes, the report said.
Shehbaz Sharif first became Chief Minister of Punjab province in 1997 when his brother Nawaz Sharif was the Prime Minister of Pakistan.
Following General Pervez Musharraf's coup in 1999 toppling the Nawaz Sharif government, Shehbaz Sharif along with the family spent eight years in exile in Saudi Arabia before returning to Pakistan in 2007.
He became Pakistan's Punjab Chief Minister for the second term in 2008 and he grabbed the same slot for the third time in 2013.
"My family lost PKR 2 billion because of my decision. I am telling you the reality. When my son's ethanol production plant was being set up, I still decided to impose a duty on ethanol. My family lost PKR 800 million annually because of that decision. The previous government withdrew that notification stating that it was injustice with the sugar mills," he claimed.
The Prime Minister's counsel argued that the laundering case was "politically motivated" and "based on mala fide intentions" by the erstwhile government headed by Imran Khan.
During the previous hearing on May 21, the special court had issued arrest warrants against Suleman Sharif, in the case after extending the interim bails of Shehbaz Sharif and Hamza Sharif till May 28.
@FATFNews
Pakistan and Nicaragua have been removed from the FATF’s Jurisdictions under Increased Monitoring list, often referred to as the 'grey list'. See the full update on the list here➡️ https://bit.ly/3Dj3K9S #FollowTheMoney
https://twitter.com/FATFNews/status/1583499858123448330?s=20&t=pb7ZmsupBVCjSyrdMKknbA
-------------
Paris, 21 October 2022 - Jurisdictions under increased monitoring are actively working with the FATF to address strategic deficiencies in their regimes to counter money laundering, terrorist financing, and proliferation financing. When the FATF places a jurisdiction under increased monitoring, it means the country has committed to resolve swiftly the identified strategic deficiencies within agreed timeframes and is subject to increased monitoring. This list is often externally referred to as the “grey list”.
The FATF and FATF-style regional bodies (FSRBs) continue to work with the jurisdictions below as they report on the progress achieved in addressing their strategic deficiencies. The FATF calls on these jurisdictions to complete their action plans expeditiously and within the agreed timeframes. The FATF welcomes their commitment and will closely monitor their progress. The FATF does not call for the application of enhanced due diligence measures to be applied to these jurisdictions. The FATF Standards do not envisage de-risking, or cutting-off entire classes of customers, but call for the application of a risk-based approach. Therefore, the FATF encourages its members and all jurisdictions to take into account the information presented below in their risk analysis.
The FATF identifies additional jurisdictions, on an on-going basis, that have strategic deficiencies in their regimes to counter money laundering, terrorist financing, and proliferation financing. A number of jurisdictions have not yet been reviewed by the FATF or their FSRBs, but will be in due course.
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the FATF has provided some flexibility to jurisdictions not facing immediate deadlines to report progress on a voluntary basis. The following countries had their progress reviewed by the FATF since June 2022: Albania, Barbados, Burkina Faso, Cambodia, Cayman Islands, Haiti, Jamaica, Jordan, Mali, Morocco, Myanmar, Nicaragua, Pakistan, Panama, Philippines, Senegal, South Sudan, Türkiye, UAE, and Uganda. For these countries, updated statements are provided below. Gibraltar chose to defer reporting; thus, the statement issued in June 2022 for that jurisdiction is included below, but it may not necessarily reflect the most recent status of the jurisdiction’s AML/CFT regime. Following review, the FATF now also identifies the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Mozambique, and Tanzania.
The FATF welcomes the progress made by these countries in combating money laundering and terrorist financing, despite the challenges posed by COVID-19.
Pakistan
The FATF welcomes Pakistan’s significant progress in improving its AML/CFT regime. Pakistan has strengthened the effectiveness of its AML/CFT regime and addressed technical deficiencies to meet the commitments of its action plans regarding strategic deficiencies that the FATF identified in June 2018 and June 2021, the latter of which was completed in advance of the deadlines, encompassing 34 action items in total. Pakistan is therefore no longer subject to the FATF’s increased monitoring process.
Pakistan will continue to work with APG to further improve its AML/CFT system.
1,
This thread is From a WikiLeaks cable dated January 24, 2007,
documenting a meeting between Mohammed bin Zayed Al Nahyan (MBZ), then Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi and now President of the UAE, and R. Nicholas Burns, the U.S. Under Secretary of State for Political Affairs at
Show more
Warfare Analysis
@warfareanalysis
·
Oct 31
2, MBZ views on free elections: “Middle East is not California”
"MBZ: if we want to make peace." In "The Middle East," he insisted, "is not
California." In the post 9/11 world "in any Muslim country you will
see the same result." While members of the U.S. Congress and
Show more
Warfare Analysis
@warfareanalysis
·
Oct 31
3, MBZ views on Quran schools: MBZ calls Quran schools “some Taliban schools”
“Correcting the situation required education, according to MbZ, a process that will take 25 to 50 years of focused effort to turn around deeply-rooted cultural phenomena.
In the western part of
Show more
Warfare Analysis
4, MBZ: Muslims should never have free elections, We should worry about 3 Islamic counties: Egypt 🇪🇬, Saudi Arabia 🇸🇦 , and Pakistan 🇵🇰.
“MbZ countered that, "free elections in the Middle East" could eventually mean that the U.S. would "have to find
somewhere else to get 17 million barrels (of oil) a day."
In Iraq, MbZ said, elections had produced "a disaster."
As for the rise of Islamic fundamentalism and pressure from jihadists inspired by Iran,
he said he was not worried about the UAE, which could hold out for a
long time: "The Iranians will have a hard time coming here, but we
will lose Arab countries like Lebanon and Palestine.
Thank God for Hosni Mubarak (described as a family friend of the Al Nahyan).
If Egypt has free elections, they will elect the Muslim Brothers."
There were three large Islamic countries to worry about, according to
MbZ: Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and Pakistan.”
https://x.com/warfareanalysis/status/1984515658084704702
---------------------
Warfare Analysis
@warfareanalysis
6, MBZ calls Muslim scholars “some holy man in Mecca”
“Referring to the UAE situation, MbZ opined that of the 60,000
soldier UAE armed forces and its loyalties, some 50 to 80% would
respond to a call of "some holy man in Mekkah."
He repeatedly alluded to being "stoned" by his own citizens if he pushed some
subjects too openly.
Acknowledging the prodding by the U.S. to hold elections, MbZ said the process would take at least 20 years and that focus should be on the next generation.
"When I travel to Saudi
Arabia, I meet with 80-85 year old Saudi leaders who never learned of
the internet until they were 70. There is a big gap in Saudi
Arabia." MbZ said the UAE is addressing the educational aspect of
the problem by privatizing government schools with the aim of
privatizing 25% in 5 years so that there will eventually be 0%
"talebani Quran schools."”
https://x.com/warfareanalysis/status/1984515669862293546