US Census Update: Pakistani-Americans' Average Annual Household Earnings Estimated at $150,000
The average annual household earnings of Pakistani-Americans are $149,178, according to the latest update issued by the United States Census Bureau for 2022. The update estimates the median income of 132,958 Pakistani-American households at $106,281. Average is calculated by adding up all incomes and dividing it by total number of households. Median income level divides the top 50% of families from the bottom 50%. It shows that Pakistani-American household incomes are roughly at par with the Asian-American households' median of $104,646 and average of $149,363. The highest income ethnic group in the US are Asian Indian households with a median of $152,341 and average of $197,732. Asians are significantly richer than Whites (mean $78,636, average $112,415) and African Americans (mean $52,238, average $76,888). The word "alone" in the labels in the following table excludes mixed race households.
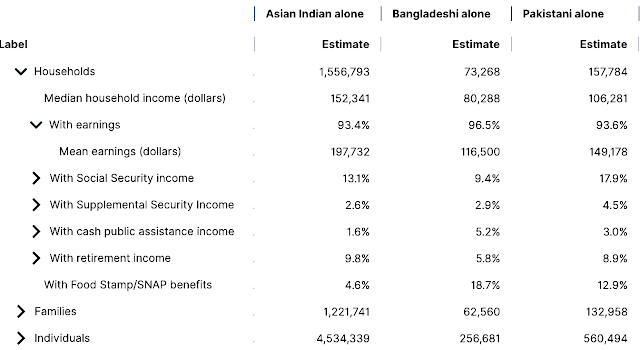 |
| South Asian Americans Households. Source: US Census Update 2022 |
Asian Americans are the best educated racial group in the United States. From 2012 to 2022, the percentage of adults age 25 and older with a bachelor’s degree or more increased from 34.5% to 41.8% for the non-Hispanic White population; from 21.2% to 27.6% for the Black population; from 51% to 59.3% for the Asian population; and from 14.5% to 20.9% for the Hispanic population, according to the US Census.
 |
| Educational Attainment By Racial Groups (Source: US Census) |
Among Asian Americans, the Indians (three quarters) have the highest educational attainment with at least a bachelor's degree, followed by Koreans and Pakistanis (about 60%), followed by the rest.
 |
| Asian American Educational Achievement by Countries of Origin. Source: US Census |
Asians, including Chinese/Taiwanese, Indians and Pakistanis, tend to be concentrated in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Technology) fields where incomes are generally much higher than in other occupations.
As of 2019, there were 35,000 Pakistan-born STEM workers in the United States, according to the American Immigration Council. They included information technologists, software developers, engineers and scientists. These figures do not include medical doctors and healthcare workers.
 |
| Foreign-Born STEM Workers in America. Source: American Immigration Council |
Foreign-born workers make up a growing share of America's STEM workforce. As of 2019, foreign-born workers made up almost a quarter of all STEM workers in the country. This is a significant increase from 2000, when just 16.4% of the country’s STEM workforce was foreign-born. Between 2000 and 2019, the overall number of STEM workers in the United States increased by 44.5 percent, from 7.5 million to more than 10.8 million, according to American Immigration Council.
 |
| India and Pakistan Among Top 10 Countries Receiving US Immigrant Visas. Source: Visual Capitalist |
India topped the top 10 list of foreign-born STEM workers with 721,000, followed by China (273,000), Mexico (119,000), Vietnam (100,000), Philippines (87,000), South Korea (64,000), Canada (56,000), Taiwan (53,000), Russia (45,000) and Pakistan (35,000). Enormous number of Indian STEM workers in the United States can at least partly be attributed to the fact that India's "body shops" have mastered the art of gaming the US temporary work visa system. Last year, Indian nationals sponsored by "body shops" like Cognizant, Infosys and TCS received 166,384 H1B visas for work in the United States. By comparison, only 1,107 Pakistanis were granted H1B visas in Fiscal Year 2022. In addition to H1B work visas, 9,300 Indian nationals and 7,200 Pakistani nationals received immigrant visas to settle in the United States as permanent residents in 2021.
 | |
|
In addition to 35,000 Pakistan-born STEM workers, there were 12,454 Pakistan-born and Pakistan-trained medical doctors practicing in the United States, making the South Asian nation the second largest source of medical doctors in America. Pakistan produced 157,102 STEM graduates last year, putting it among the world's top dozen or so countries. About 43,000 of these graduates are in information technology (IT).
 |
| H1B Visas Issued in Pakistan. Source: Visagrader.com |
Every year, applicants sponsored by Indian body shops claim the lion's share of H1B visas. In 2022, Indians received 166,384 new H1B visas, accounting for nearly three quarters of all such visas issued by the US government. The figures reported as India IT exports are in fact the wages earned by millions of Indian H1B workers in the United States.
Many developing countries are experiencing brain drain. But India is losing its best brightest at a much faster rate than others. Some call it "The Great Indian Brain Drain". This is the reason why Indians in the United States are the best educated and the highest earning group. In a recently published book titled "The Other One Percent", authors Sanjoy Chakravorty, Devesh Kapur and Nirvikar Singh explain this phenomenon.
They write that the vast majority of Indians who migrate to the United States are from privileged backgrounds in terms of caste, class and education. They have gone through “a triple selection” process that gave Indian-Americans a boost over typically poor and uneducated immigrants who come to the United States from other countries. The first two selections took place in India. As explained in the book: “The social system created a small pool of persons to receive higher education, who were urban, educated, and from high/dominant castes.” India’s examination system then selected individuals for specialized training in technical fields that also happened to be in demand in the United States. Kapur estimated that the India-American population is nine times more educated than individuals in the home country. Here's an excerpt of it:
"A major focus of this book is on demonstrating and understanding the multiple selections that shaped the Indian-American population. These selections applied not only to education (that, in terms of attaining college degrees, made the India-born population three times more educated than that in the host country and nine times more educated than the home country’s population) but also to class and caste (favoring, by large margins, the “upper” and dominant classes and castes of India), profession (engineering, IT, and health care), and both the region of origin (Gujarati and Punjabi were overrepresented in the first two phases, and Telugu and Tamil in the third phase) and region of settlement (in specific metropolitan clusters in and around New York City, the San Francisco Bay Area, Chicago, Washington, D.C., and Houston and Dallas). In addition to direct selection is what we call the “selection+” advantage: we suggest that group characteristics or norms, such as the fact that Indians had the highest propensity to live in married-couple households of any major immigrant group, added to the advantages of being an already selected group. We show, in particular, how family norms were useful in keeping the Indian-American poverty level low (under 5 percent) and family income high (the highest in the United States). It is also likely that the selection process enabled, without explicitly intending to, the generation of high levels of social capital (through linguistic/ professional networks such as Gujarati entrepreneurs in the hotel industry, Telugu and Tamil workers in the IT industry, IIT engineers, Malayali nurses, Bengali academics, etc.)"
Related Links:
2021: A Banner Year For Tech Startups in Pakistan
Pakistani-Americans in Academia
Top One Percent: Are Hindus the New Jews in America?
Growing Share of Working Age Population in Pakistan
Pakistan Scientific Output is World's Fastest Growing
India's Chandrayaan 3 Success: Can Pakistanis Explore Space?
Digital Pakistan 2022
Pakistan's Large and Growing Civil Nuclear Program
Riaz Haq's Youtube Channel




Comments
https://www.cbsnews.com/news/american-income-wealth-surged-pandemic-federal-reserve/
The racial group with the highest median wealth are Asian American households, with about $536,000 in assets. The Fed found that even as wealth inequality declined during the pandemic, income disparities worsened. Median incomes grew 3% compared with the previous survey, which covered 2017 through 2019.
--------------
Many Americans saw major gains in their wealth during the pandemic, boosted by rising home and investment values as well as federal stimulus payments, according to a new report from the Federal Reserve.
The net worth of the median U.S. household — the midpoint between the richest and poorest households — surged 37% to $192,900 between 2019 and 2022, according to the Survey of Consumer Finances, published by the central bank on Wednesday. The survey, issued every three years, provides insights into the financial health of households by examining income, wealth and debt.
Millions of households saw their wealth jump during the pandemic thanks to gains in the value of their homes and investments. Even people who rent their homes, and thus were locked out of the dizzying rise in real estate values since 2019, saw a bump in median wealth.
The pandemic-induced recession, which was short and brutal, cost 20 million jobs, but the rapid recovery, fueled by relief such as stimulus checks and extra unemployment aid, helped bolster many households. Gains were widespread across ages, races and education levels, the Fed said.
"Increases in both median and mean net worth were near universal across different types of families, grouped by either economic or demographic characteristics," the bank said in its analysis of the data.
The boost to many families' wealth helps explain the robustness of the economy this year, despite a flurry of interest rate hikes from the Fed that have made it more expensive to buy everything from homes to cars. Economists had been warning that the rate hikes could push the U.S. into a recession, but so far that hasn't happened.
Greater Wealth, Greater Uncertainty: Changes in Racial Inequality in the Survey of Consumer Finances
https://www.federalreserve.gov/econres/notes/feds-notes/greater-wealth-greater-uncertainty-changes-in-racial-inequality-in-the-survey-of-consumer-finances-20231018.html
Wealth by Race in 2022
This note explores patterns in families' wealth, income, and financial well-being across race and ethnicity using new data from the 2022 Survey of Consumer Finances (SCF).2 We first document continued large and persistent differences in wealth across race and ethnicity, with particular attention to how such differences changed between the 2019 and 2022 surveys. We then turn to analyzing other metrics of financial well-being, including income, ability to meet payments on recurring monthly expenses, and families' expectations and attitudes about their financial situations.
Figure 1 shows large disparities in real wealth—the difference between assets and liabilities—across families of different races in 2022.3,4 Median wealth (the amount held by a typical family, shown in the top panel) among White families was $285,000 in 2022. By comparison, the typical Asian family—who we can split out for the first time in 2022 because of an oversample of certain non-White groups—held $536,000, nearly twice that of the typical White family.5 Meanwhile, the wealth of the typical Black family ($44,900) was only about 15 percent of the typical White family. The typical Hispanic family similarly held only about 20 percent of the wealth of the typical White family (about $61,600). The remaining families—a diverse group that includes those identifying as American Indian, Alaska Native, Native Hawaiian, Pacific Islander, other race, and all respondents reporting more than one racial identification—had median wealth similar to the typical Black or Hispanic family, rather than the typical White or Asian family. Notably, mean wealth (the average within each group, shown in the bottom panel; note the different vertical axis scale) was much higher than medians, particularly for White and Asian families. This reflects the fact that mean wealth is influenced significantly by a small number of very rich families, which tend to be comprised disproportionately of White and Asian families.
https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/personalandhouseholdfinances/incomeandwealth/articles/householdwealthbyethnicitygreatbritain/april2016tomarch2018
White households median £313,900 mean £590,400
Indian households median £313,200 mean £493,800
Pakistani households median £224,500 mean £302,100
Chinese households median £77,300 mean £348,400
Bangladeshi households median £65,600 mean £141,100
Other Asian households median £162,100 mean £367,800
Black Caribbean households median £85,900 mean £379,200
It explains that the vast majority of Indians who migrate to the United States are from privileged backgrounds in terms of caste, class and education. They have gone through “a triple selection” process that gave Indian-Americans a boost over typically poor and uneducated immigrants who come to the United States from other countries. The first two selections took place in India. As explained in the book: “The social system created a small pool of persons to receive higher education, who were urban, educated, and from high/dominant castes.” India’s examination system then selected individuals for specialized training in technical fields that also happened to be in demand in the United States. Kapur estimated that the India-American population is nine times more educated than individuals in the home country.
Here's an excerpt of it:
A major focus of this book is on demonstrating and understanding the multiple selections that shaped the Indian-American population. These selections applied not only to education (that, in terms of attaining college degrees, made the India-born population three times more educated than that in the host country and nine times more educated than the home country’s population) but also to class and caste (favoring, by large margins, the “upper” and dominant classes and castes of India), profession (engineering, IT, and health care), and both the region of origin (Gujarati and Punjabi were overrepresented in the first two phases, and Telugu and Tamil in the third phase) and region of settlement (in specific metropolitan clusters in and around New York City, the San Francisco Bay Area, Chicago, Washington, D.C., and Houston and Dallas). In addition to direct selection is what we call the “selection+” advantage: we suggest that group characteristics or norms, such as the fact that Indians had the highest propensity to live in married-couple households of any major immigrant group, added to the advantages of being an already selected group. We show, in particular, how family norms were useful in keeping the Indian-American poverty level low (under 5 percent) and family income high (the highest in the United States). It is also likely that the selection process enabled, without explicitly intending to, the generation of high levels of social capital (through linguistic/ professional networks such as Gujarati entrepreneurs in the hotel industry, Telugu and Tamil workers in the IT industry, IIT engineers, Malayali nurses, Bengali academics, etc.). Several linguistic subgroups, many with caste or clan affinities, with moderate to high levels of human capital, were also successful in creating “bonding” social networks and capital that enhanced their status.5 Even low-income groups, such as Punjabi
taxi drivers in New York, were able to create some social (bonding) capital. Several professional subgroups without kinship or linguistic affiliation—doctors and engineers, for example—were able to organize and prosper by creating bridging social networks and capital. Selection—broadly understood—is present as a primary or secondary theme in much of this book.
https://www.census.gov/newsroom/press-releases/2023/educational-attainment-data.html#:~:text=the%20Hispanic%20population.-,From%202012%20to%202022%2C%20the%20percentage%20of%20adults%20age%2025,20.9%25%20for%20the%20Hispanic%20population.
---------------
Over three-quarters of the Asian Indian (76.3%) and over half of the Korean (59.3%), Pakistani (58.2%), Chinese except Taiwanese (56.5%), and Japanese populations *53.5%) had a bachelor’s degree or higher.
The Cambodian (24.2%), Vietnamese (32.1%) and Hmong (23.6%) alone and alone or in any combination populations had the largest shares of high school diploma (or equivalency) attainment only.
https://www.census.gov/library/stories/2023/06/detailed-characteristics-race-ethnic-tribal-groups.html
https://carnegieendowment.org/2021/06/09/social-realities-of-indian-americans-results-from-2020-indian-american-attitudes-survey-pub-84667
Thirty percent of non-citizen IAAS respondents possess a green card (or a permanent residency card), which places them on a pathway to gaining U.S. citizenship. Twenty-seven percent are H-1B visa holders, a visa status for high-skilled or specialty workers in the United States that has historically been dominated by the technology sector. On average, an H-1B visa holder reports living in the United States for eight years, although 36 percent of H-1B beneficiaries report spending more than a decade in the country (that is, they arrived before 2010). Eighteen percent of non-citizens reside in the United States on an H-4 visa, a category for immediate family members of H-1B visa holders. Fourteen percent of non-citizens are on F-1, J-1, or M-1 visas—categories of student or scholar visas—while another 5 percent hold an L-1 visa, a designation available to employees of an international company with offices in the United States. A small minority of non-citizen respondents—6 percent—claim some other visa status.
------------------------
The overwhelming majority of Hindus with a caste identity—more than eight in ten—self-identify as belonging to the category of General or upper caste.
White America crafted a tempting story to explain the ascent of Asian Americans—“an important racial minority pulling itself up from hardship and discrimination to become a model of self-respect and achievement,” as a 1966 article in U.S. News & World Report described Chinese Americans. Those once seen as “Yellow Peril” and “Dusky Peril” became a “model minority,” creating a new racial category: Asians were those who could assimilate into whiteness but maintain a distinct cultural identity. In America, riches await, and with a little grit, anyone can reap them. The story tempered the racial progress of the civil-rights era, as if to tell Black people: If those Asians can be so successful, why can’t you? Racism was a part of America’s sordid past. The success of these new Asians proved that. Indian Americans have since been allotted a specific prominence within the context of this story. In 2009, the year I graduated from college, an article in Forbes declared Indian Americans “the new model minority,” hailing families like ours as “the latest and greatest ‘model.’ ” Within a little more than a generation, Indian Americans have become one of the wealthiest and most highly educated immigrant groups in the country, earning a median income of more than one hundred thousand dollars. The steep ascent of Indian Americans reified the pernicious model-minority myth. They called us exceptional. We fulfilled their prophecy. But the story of our subcommunity’s rise wasn’t one of genetics, nor can it simply be explained by work ethic, as pundits may have one believe. The true story, as described in The Other One Percent: Indians in America, is largely due to a rigorous but invisible selection process that often begins in India itself. In India’s highly stratified society, middle- and upper-class Indians from dominant castes typically access the best schools and jobs that feed into opportunities in America, which favor immigrants who bring specialized skills in tech and science. The result: an American diasporic community that is roughly nine times more educated than Indians in India. These conditions enabled Indian families like ours—families that had been thrice-filtered and stratified—to prosper like few other immigrant groups have ever done in America. Even though pockets of Indian Americans still struggle, this insular group has become the poster image for America’s post-racial fantasy.
@0x_ale
The hidden truth about India's brain drain?
It's not just about loss, but transformation.
Sometimes the biggest exports aren't products.
They're people who change the world.
This is the new “oil” that nations will compete for.
https://x.com/0x_ale/status/1874897365133643808
----------------------
Alessandro Palombo
@0x_ale
This is India:
- 11% of Fortune 500 CEOs
- 90+ unicorn founders are Indian-born
- 1/3 of all engineers in Silicon Valley are from India
Why have they all left India to succeed?
Here's the hidden truth about the world's most controversial brain drain 🧵:
https://x.com/0x_ale/status/1874896954771329162
-------
Alessandro Palombo
@0x_ale
First, let's understand the scale of this exodus:
- 1.3M Indians left between 2015-2022
- 225,000 renounced citizenship in 2022 alone
- 1.5M Indian students studying overseas
This isn't just migration…it's a transformation of global leadership.
https://x.com/0x_ale/status/1874897002905096520
-----------------
Alessandro Palombo
@0x_ale
The economic impact is staggering:
- IT sector missing $15-20B yearly potential
- Shortage of 2.4M doctors
- $160B lost annually to brain drain
For perspective:
That's more than India's entire defense budget (~$74.3B).
https://x.com/0x_ale/status/1874897020563140714
-----------------
Alessandro Palombo
@0x_ale
Look at the paradox:
India simultaneously:
- Leads global tech companies
- Produces top innovators
- Creates world-class talent
Yet struggles to keep any of them.
The reason? There are a few key factors…
https://x.com/0x_ale/status/1874897054474117197
----------------
Alessandro Palombo
@0x_ale
The reality on the ground:
- 7.33% unemployment rate (2022)
- Significantly lower wages than global standards
- Limited R&D investment
- Restricted innovation opportunities
This creates a powerful push factor.
https://x.com/0x_ale/status/1874897120765132863
-------------------
Alessandro Palombo
@0x_ale
But here's where it gets interesting…
While India loses talent, it gains something else:
- Massive remittance inflows
- Global knowledge transfer
- International influence
A hidden advantage that will only strengthen as global mobility increases
https://x.com/0x_ale/status/1874897153983926344
----------------
Alessandro Palombo
@0x_ale
The story is clear:
- Microsoft
- Google
- Adobe
- IBM
All run by Indians who left India.
But now something fascinating is happening...
https://x.com/0x_ale/status/1874897170282975581
https://x.com/leonardaisfunE/status/1888428850314702978
https://x.com/jakeshieldsajj/status/1887568815313330253
---------------
H-1B Hate Speech Against Indians Sparks Outrage: Far-Right Host Stew Peters’ Racist Tirade Goes Viral - '... Third World Parasites'
https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/world/us/h-1b-hate-speech-against-indians-sparks-outrage-far-right-host-stew-peters-racist-tirade-goes-viral-third-world-parasites/amp_articleshow/116781139.cms
A video of far-right commentator Stew Peters and comedian Leonarda Jonie spewing hate against Indian immigrants has sparked widespread condemnation online. Peters, known for his inflammatory rhetoric, posted the video on X with the caption: "This is the culture we’re importing through 'qualified H1-B visa' recipients."
In the video, Peters launched into a tirade, calling Indians “cockroaches and parasites,” accusing them of "not assimilating into American culture" and making vile claims about their hygiene and moral values. Jonie, laughing along, did little to challenge Peters’ remarks, which included grotesque stereotypes and unfounded accusations.
His language was laced with vitriol as he painted a picture of Indian immigrants as a threat to American society. He went on to mock Indian cultural practices, including accusing them of brushing their teeth with the same material they use to eat soup
https://www.ndtv.com/world-news/new-h-1b-approvals-for-indian-it-fall-to-4-573-lowest-in-10-years-9728775
The number of first-time H-1B visa applications approved for major Indian IT companies has fallen drastically to just 4,573 --the lowest in the last 10 years. As compared to 2015, the figure has gone down substantially by 70 per cent and by 37 per cent as compared to 2024.
According to data collected by the National Foundation for American Policy (NFAP) from the US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) H-1B Employer Data Hub, new H-1B approvals for leading Indian IT service providers witnessed a dramatic fall.
The only Indian organisation in the top five US employers of H-1B workers was Tata Consultancy Services (TCS). It managed to get the lion's share among the top seven IT firms, according to The Times of India.
Compared to 1,452 in 2024 and 1,174 in 2023, TCS obtained 846 initial employment clearances in FY 2025. In contrast, TCS reported 5,293 approvals for "continuing-employment," which covers visa renewals for current H-1B holders.
However, their extension rejection rate increased to 7 per cent (from 4 per cent in 2024). The overall firm-wide continuing-employment rejection rate remained low at 1.9 per cent.
This sharp decline in new H-1B entries, along with rising rejections or fall in initial employment files, points to a larger structural shift in the way overseas tech recruitment is conducted.
According to the survey, employers are putting more emphasis on keeping current employees in the United States instead of recruiting new talent from elsewhere.
The top four slots for new H-1B approvals are now occupied by US-based digital titans like Amazon, Meta, Microsoft, and Google for the first time — highlighting the change in the visa environment away from outsourcing-driven Indian companies and towards major American competitors.
The majority of H-1B applications are petitions for continued employment, and most major IT services companies continue to have low rejection rates. The list of the top 25 employers for initial H-1B applications includes only three Indian enterprises.
Rejection rates for continuing-employment petitions ranged from 1 per cent to 2 per cent, according to Infosys, Wipro, and LTIMindtree. However, FY 2025 witnessed a substantial increase in first employment rejections.
TCS has one of the lowest rejection rates among big companies (2 per cent), followed by HCL America (6 per cent), LTIMindtree (5 per cent), and Capgemini (4 per cent).
According to immigration portal Beyond Border, approvals for people categorised as "software engineers" in the labour-certification stage have been declining for four years running.
Labour certifications in this category decreased from 40,378 in 2022 to 23,922 through the third quarter of 2025, according to H1BGrader.